A STUDY OF THE ENZYMATIC ACTIVITY OF INNATE IMMUNITY CELLS UNDER THE EFFECT OF FSCs №1 AND №2

The scientific study of the effect of FSCs №1 «ANTI-PARASITE» and №2 « DETOX » on immunity.
Hereafter is the translation of the studies carried out by Dr Plekhova, Head of Research at the Laboratory of Cell Biology in Vladivostok, Russia.
N.G. Plekhova, PhD, MD (Biology), Head of Research at the Laboratory of Cell Biology and Pathohistology, Somov Research Institute of Epidemiology and Microbiology (a state-owned establishment), Vladivostok.
L.I. Radikova, doctor and physiotherapist, Vladivostok.
“In 1955, the German doctor Hans-Heinrich Reckeweg formulated his theory of homotoxicology. According to this theory, disease is how the organism reacts when it is exposed to different toxins. Dr Reckeweg defined 6 phases of homotoxicosis. The first 3 are seen as relating to the tissue (reversible) and the others as relating to the cells (irreversible or reversible with difficulty).
As a result of the various help that it is given during the first 3 phases, the organism recovers a normal state of physiological homeostasis. When it passes into the next phases, the toxins that have built up in the tissue of the organs enter the cells to destroy them, so giving rise to functional problems. At this point appear conditions like cysts, fibromas, papillomas, adenomas, thrombophlebitis, tumours, etc., as well as adipose deposits and illnesses related to the connective tissue of the organs. This becomes apparent in the form of pathological processes: rheumatism, polyarthritis, in the course of which uric acid, which is the result of poor absorption of protein by the organism, accumulates in the joints and the muscles. The final phase of homotoxicosis sees the development of irreversible diseases linked to the dedifferentiation of cells and organs, and happens when the anticancer defence, which ensures the enzymatic capacity of the large intestine, is non-existent and when pathological cells start forming and developing without being constrained. Toxins accumulate in the organism as a result of a disorder pertaining to the metabolism and the working of the enzymatic systems, but also as a result of the activity of different types of pathogenic micro-organisms (viruses and bacteria) and macro-organisms (intestinal parasites, etc.), as well as exterior factors such as air and water pollution, the contamination of food, etc.
The immune system forms part of the organism’s main defence mechanism. It can identify and destroy pathogens. The organism has two types of immune response: the innate and the adaptive. Innate immunity consists first and foremost of phagocytic cells (neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, tissue cells or mast cells) and natural killer cells.
The life span of neutrophils is very short but they are extremely numerous. Their role is to trigger the destruction of extracellular pathogens and their toxins and to trigger the inflammatory process. These cells are the main actors in the acute inflammatory phase. Whereas another group of monocyte-derived cells – macrophages, are cells which are long-lived. Apart from the fact that they are professional phagocytes, they are antigen-presenting cells which mark the transition from the acute to the chronic inflammatory phase.
The aim of this study is to examine the effects of Functional State Correctors №1 and №2 on innate immunity cells and on salmonella bacteria (Salmonella enteritidis).
The Functional State Correctors were brought into contact separately with Salmonella enteritidis micro-organisms after 30 and 60 minutes; their life span was determined with the help of a specific dye – acridine orange. The fluorescence technique in preparations, based on Bertalanffy’s method, means that by using this dye it is possible to carry out a study of the bacteria which is both morphological and cytochemical.
In order to evaluate the morphology of the bacteria, fluorescence microscopy on the preparations was carried out respecting the following conditions of fluorescence: length of the excitation wavelength: 430 nm, barrier filter: 515 nm. A primary culture of neutrophils and blood monocytes/macrophages was used as a model. A fraction of adherent cells was obtained from peripheral venous blood injected with heparin (10 U/ ml).
As for the cells which had not undergone the effects of the Functional State Correctors, they were used as control samples. After being exposed, the cells were air-dryed and fixed in formalin vapours for 15 min.
Arguments and Results
In accordance with the method used to detect the viability of the bacteria dyed with acridine orange, the micro-organisms containing intact DNA are coloured in green. The specificity of cytochemical staining by means of this dye on the DNA is determined by the effect on the nucleic acids of a specific enzyme: desoxyribonuclease. Under its effect, the DNA of the bacteria breaks up, the green luminescence disappears and a yellow luminescence appears signalling the presence of destroyed DNA in the bacteria. The study of the antibacterial properties of the correctors showed that Functional State Correctors №1 and №2 had a cytostatic reaction on the Salmonella enteritidis bacteria, i.e. they are able to stop the cell division of these bacteria.
The strongest effect was seen under the action of Functional State Corrector №2 for 60 min. Not only did the quantity of DNA bacteria destroyed increase, but their morphology was also modified. Under the effect of Functional State Corrector №2, bacilliform micro-organisms (sch. 1a) changed into cocciform micro-organisms (sch. 1c, 1d), indicating their transition from an active state of multiplication to a spherical state, i.e. to a state of rest.
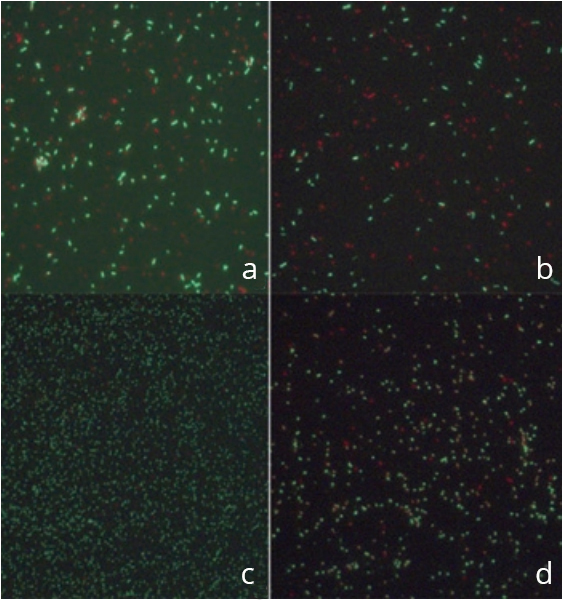
The study of the enzymatic activity of the cells on the bacteria, before being exposed to the phagocytes which had undergone the effect of the Functional State Correctors for 30 and 60 minutes, showed a marked difference (р<0.05) in the stimulation indexes.
It was established that Functional State Corrector №1 stimulated the enzymatic activity of innate immunity cells, in particular the exoenzymes of the cell membrane after being applied for 30 minutes.
The analysis of the effect of Functional State Corrector №2 highlighted a stimulation of the phagocytes revealed by high indexes of enzymatic activity in comparison to the cells contaminated by Salmonella enteritidis.
There was an unquestionable increase in the activity of the neutrophils and macrophages under the influence of Functional State Corrector №2 (р<0.01)
It can therefore be seen that our data is a representative example of an accentuated antibacterial action on salmonella, moreover, Functional State Corrector №2 has a strong cytotoxic effect (preventing division) compared to Functional State Corrector №1.
In addition to what has been mentioned above, the complete study of the enzymatic activity of innate immunity cells underlined that Functional State Correctors had a very marked stimulating effect on them. Moreover, in the event of these cells becoming contaminated by bacteria, it was observed that the Functional State Correctors had a strengthening effect on the antibacterial activity of the phagocytes.
Everything that has been stated above highlights how Functional State Correctors can be used both as immunomodulatory agents to improve the performance of the immune system as a whole, and also to increase the resistance of the organism to the pathogenic agents of infectious enteric diseases in particular. The increase in the activity of innate immunity cells makes them better able to fulfil their function of destroying not only pathogenic agents but also different damaged cell residues and contributes, thanks to Functional State Correctors №1 and №2, to the detoxification of the organism”.
Recent Posts


THE RUNES OF NEW AGE BY PROFESSOR GOCH

DETOXIFY YOUR BODY WITH FSC

WHICH FSCs ARE BEST FOR BOOSTING IMMUNE DEFENCES IN THE WINTER?

Categories
- Articles (5)
- Energy Sphere (3)
- Functional State Correctors (15)